TL;DR
- Scaling B2B referral programs is about automation, fraud control, and compliance, not just bigger rewards.
- Use hybrid incentives (small upfront + recurring) with claw-backs to protect unit economics.
- Rely on clear ToS + automated checks to fight abuse and stay legally safe.
- Keep optimizing with in-product prompts, A/B tests, and funnel metrics to sustain growth.
🤝 In the final chapter of the Guide to B2B User Referrals 2.0, we collaborated with Linus Hallberg, Senior Product Manager at Typeform, to explore strategies for scaling and maintaining b2b user referral programs. Linus implemented and successfully scaled the user referral program at Typeform and shares his experience and best practices. This piece will also shed light on legal and tax implications by Martin Friedberg (partner at CMS and specialized in tax law).
Scaling a B2B user referral program is a complex challenge that most teams underestimate. Running a referral program in-house requires extensive resources, especially when handling fraud prevention, payout automation, and compliance across multiple regions.
Scaling a B2B referral program comes down to two options:
- In-house management – Offers full flexibility but requires significant resources on the engineering side for tracking, fraud prevention, compliance, and payouts.
- Third-party tools – Provide automation but rarely cover everything end-to-end, leaving gaps in fraud detection, tax compliance, and payout handling.
Many third-party tools promise automation, but few can truly scale without manual oversight. As referral volume grows, so do the risks of errors, inefficiencies, and legal liabilities. Choosing the right approach depends on your ability to manage complexity while ensuring a seamless, scalable program. Read our in-depth comparison of buying vs. building a referral program to learn more.
A successful scaling strategy for B2B referral programs requires addressing three critical areas: (1) operational complexity, (2) regulatory compliance, and (3) continuous optimization. Without a clear approach, referral programs can become high-maintenance and prone to tracking failures, inaccurate payouts, and fraud. This chapter explores the most common pitfalls and how to build a scalable, compliant, and high-performing referral program.
Why does my referral software not scale?
Even well-structured referral programs face challenges when scaling. High referral volumes introduce operational inefficiencies, compliance risks, and reward-tracking issues that can negatively impact user trust.
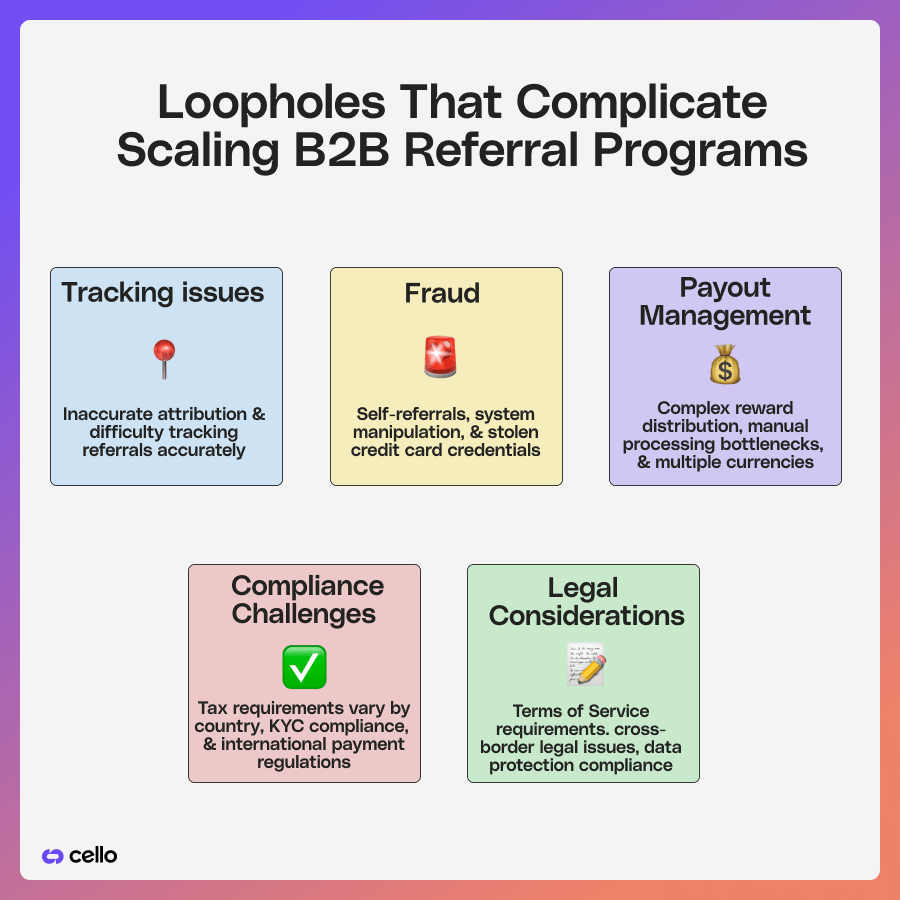
One of the biggest obstacles is the high maintenance required to keep the program running smoothly. Without automation, teams struggle with tracking referrals accurately, verifying eligibility, and ensuring rewards are distributed on time. Manually processing referrals is not only time-consuming but also prone to human error. As a result, discrepancies in tracking and attribution can lead to missed payouts, referrer dissatisfaction, and even churn.
Fraud is another common issue that grows with scale. Self-referrals, usage of stolen credit card credentials, and duplicate sign-ups can dilute the effectiveness of the program. Without proper fraud detection mechanisms, businesses may find themselves rewarding users who manipulate the system.
A well-structured referral reward system can serve as a natural fraud prevention mechanism while ensuring a positive ROI. Instead of offering a high one-time payout (e.g., €500), implementing a recurring reward model—such as a percentage of the referred customer's monthly subscription fee (e.g., 25%, capped at €500)—ensures that the company consistently generates more revenue than it distributes in rewards. This keeps the referral program profitable at all times.
Moreover, in cases of detected fraud, payouts can simply be halted, minimizing risk. An additional safeguard is introducing a claw-back period of 14 to 30 days before processing payouts, allowing time to identify fraudulent activity before any rewards are issued.
Managing reward payouts also becomes increasingly complex. For monetary incentives, businesses must handle tax compliance, process payments in multiple currencies, and ensure transactions are secure and legally compliant. Relying on manual reward distribution is cumbersome and error-prone, making it a major bottleneck when scaling.
How to handle Tax & KYC compliance for referral programs: Navigating legal and financial regulations
Monetary payouts introduce significant financial and regulatory challenges that businesses must address. Many countries require proper tax documentation, business registration, and KYC (Know Your Customer) compliance for monetary rewards. Failure to comply can result in legal issues, tax penalties, and increased operational risks.
To manage compliance, businesses often rely on payout intermediaries such as PayPal, Stripe, or Venmo. These platforms handle transactions while ensuring legal compliance (e.g., providing IRS Forms (1099-K) in the US), reducing the burden on internal teams.
However, businesses should still educate referrers about how to handle referral income from a tax perspective. The revenue generated through referrals must generally be considered as taxable income for either a private individual or a business.
Each country has specific tax thresholds that determine whether referrers must register as a business and report taxes. A few examples:
- In the United States, non-corporate referrers earning over $600 in a year must receive a 1099-MISC form.
- In Germany, individuals with a turnover of more than €25,000 in the preceding year and more than €100,000 in the current year from referrals are required to register for VAT and file a VAT return.
- In India, businesses with an annual turnover of over Rs. 20 lakh (or Rs. 10 lakh for businesses operating in northeastern states and certain hill states) must register for Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- In Israel, you should sign up as an exempt business if your annual turnover does not exceed NIS 120,000 (as of 2024).
- In the Philippines, if you are currently or are expected to earn over PHP 3,000,000 during the current taxable year, you are also required to register as a VAT taxpayer.
These are just a few examples, and it's worth noting that thresholds typically shift from year to year.
Handling payouts also involves compliance with AML (Anti-Money Laundering) laws. KYC verification is necessary to ensure users are legitimate and not engaging in fraudulent activities. If a business processes payments internally, it must verify referrers’ identities, track large transactions, and prevent suspicious activity. Partnering with KYC-compliant payment gateways as above can streamline this process and reduce legal risks.
Another major challenge is ensuring referrers receive their payouts in their local currency. While this improves user experience, it introduces foreign exchange rate fluctuations and additional processing fees. Automated systems should be in place to manage these complexities, ensuring smooth and timely payouts.
Finally, businesses must provide the correct tax documents to referrers, including credit notes, earnings statements, and withholding tax deductions if applicable. Without these safeguards, compliance becomes a significant barrier to scaling.
Legal considerations for referral programs: Terms of Service (ToS)
As referral programs scale, legal coverage must be robust enough to protect against fraud, disputes, and regulatory risks. A comprehensive Terms of Service is essential to ensure clarity around participation, reward eligibility, and payout conditions.
Enforcing the right policies is crucial to maintaining the integrity of a referral program. One key rule is the strict prohibition of self-referrals — referrers should not be allowed to create multiple accounts or falsely claim to represent the company. Additionally, referrers should be restricted from running paid ads on search or social media platforms using branded terms and using stolen credit cards to retrieve referral payouts, as this can create market confusion and drive up acquisition costs.
Fraud prevention mechanisms must be in place to detect duplicate accounts, suspicious patterns, and system manipulation. This requires a combination of automated detection and manual verification to ensure that rewards are only distributed to genuine referrers.
Cross-border payouts add another layer of complexity, as legal and compliance requirements vary by jurisdiction. Businesses must ensure:
- Referral incentives comply with local marketing regulations.
- Data protection laws, such as GDPR, are followed when processing referral data.
- Payouts align with international tax and compliance requirements to avoid legal risks.
A scalable referral program isn’t just about growth—it’s about preventing fraud, ensuring compliance, and maintaining trust.
Scaling strategies: How to optimize and grow your program
Successfully scaling a referral program requires a data-driven and iterative approach. Simply increasing payout amounts or promoting the program more aggressively won’t guarantee long-term success. Instead, businesses must focus on continuous optimization based on referral performance data.
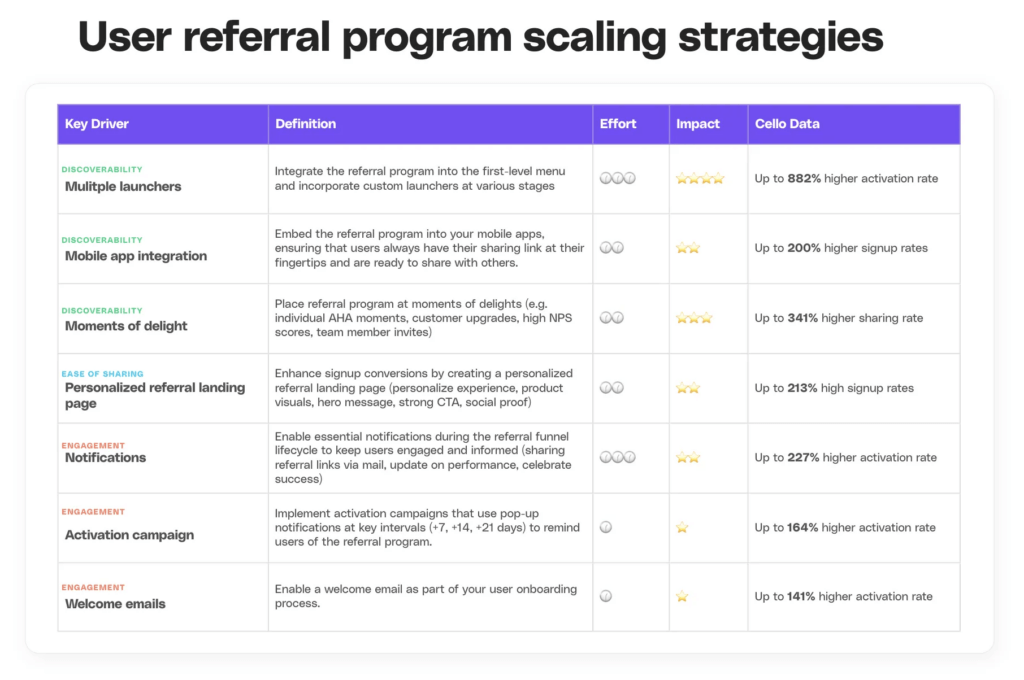
One of the most effective strategies is A/B testing. Testing different referral landing pages, email notifications, and reward structures can significantly impact conversion rates.
For example, companies like Typeform have seen dramatic improvements by refining their referral funnel. They initially sent referral invitations at moments of delight (e.g., after a successful form submission).
Later, they added a referral widget in settings, optimized their referral landing page (leading to a 12.7% signup conversion rate), and finally introduced a menu launcher that resulted in a 512% increase in referral activity within three weeks. Read more about how Typeform is using Cello to fuel their growth.
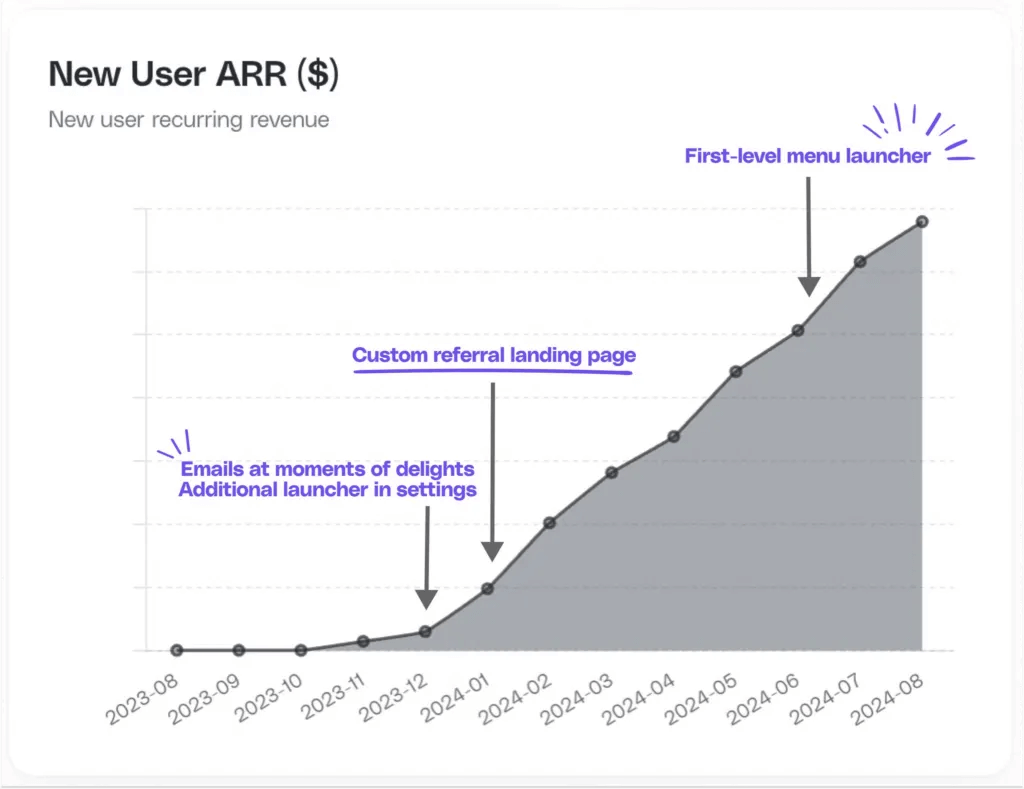
Scaling also requires leveraging data-driven decision-making. Businesses should track key metrics such as:
- Sharing Rate = % of users sharing a link with potential new users
- Unique clicks per shared link = # of potential new users who click the referral link
- Sign-Up Rate = % of potential new users clicking on the signup link for the referred tool
- Purchase Rate = % of new users converting to a paid plan
- Annualized User to Customer Conversion (AUCC) = % of new customers generated via referrals based on the total number of existing tool users (base is 1000 users)
By analyzing these metrics, businesses can refine their program to ensure maximum efficiency and ROI.
Iterative rollouts are another important tactic. Instead of launching massive program changes all at once, businesses should implement small, controlled experiments and analyze their impact before rolling out at scale.
Conclusion
Successfully scaling a referral program requires automation, compliance, fraud detection and prevention, and continuous optimization. Many businesses make the mistake of scaling too fast without addressing fraud risks, payout logistics, or tax compliance, which ultimately leads to operational bottlenecks.
To scale effectively, businesses must:
- Automate tracking, validation, and reward distribution.
- Ensure tax and KYC compliance across all payout regions.
- Continuously optimize referral funnels through A/B testing.
- Implement fraud detection and prevention mechanisms.
- Create robust ToS that protect your business
- Adopt a data-driven approach to refine and improve the program over time.
A well-executed referral program becomes a sustainable, low-CAC growth engine. However, scaling isn’t just about increasing referrals—it’s about building a system that can grow without breaking. By following these best practices, businesses can ensure that their referral program remains an effective and scalable acquisition channel for years to come.
Resources
Related Articles
The untapped channel across GTM strategies for B2B SaaS: User Referrals
Discover actionable tips & the complete process to launch your own influencer referral program

Nailing GTM for Successful B2B Referral Programs
Learn how to set the right GTM strategy for B2B SaaS user referral programs

7 Psychological Drivers of Referral Behavior to Accelerate B2B Growth
Learn how to set the right incentives for B2B SaaS user referral programs
What does it mean to “scale” a B2B referral program?
Scaling means moving from a small, manual setup to an automated, compliant, and sustainable referral system that can handle thousands of users without breaking. This includes managing payouts, fraud checks, and legal compliance.
How can I prevent fraud in referral programs?
Fraud prevention starts with identity checks, monitoring suspicious activity, and setting clear rules (e.g. no self-referrals or duplicate accounts). Many companies add claw-back periods so rewards are only paid if the referred user stays active.
When should I switch from in-house to a referral software platform?
If referrals are growing beyond manual tracking and you’re facing challenges with attribution, payouts, or fraud, it’s time to consider a third-party tool. Platforms like Cello help automate tracking, enforce rules, and manage compliance. Find out how Shore increased new MRR by 14% by migrating their in-house referral program to Cello. https://cello.so/customers/shore/
What is a “claw-back period” in referral programs?
A claw-back period is a set time (e.g. 30–90 days) before paying out rewards to ensure the referral is legitimate and the customer doesn’t churn or cancel. This protects businesses from losses.
How do I handle payouts and taxes in different countries?
To scale globally, you’ll need to comply with local tax laws (e.g. W-9 in the U.S., VAT in the EU) and possibly collect KYC documents. Many companies use referral platforms or payment processors that automate compliance.
What incentives work best for B2B referrals?
For B2B, financial rewards are common (cash, credits, discounts), but non-monetary incentives like recognition, status, or exclusive perks can be powerful motivators. Testing different rewards is key to finding the right fit.
Should I give a one-time reward or a recurring incentive?
One-time rewards are simpler and motivate initial referrals, while recurring incentives (e.g. revenue share) sustain long-term activity. A hybrid approach: small upfront bonus + recurring benefit often works best.
What are common legal considerations for referral programs?
You should create clear Terms of Service that forbid abuse (e.g. self-referrals, paid ads using your brand). You also need to comply with advertising guidelines, tax rules, and privacy laws (GDPR, CCPA).

