Key Performance Indicators, or KPIs, are a critical tool for evaluating and monitoring the performance of businesses across various industries. These measurable metrics provide insight into the success or failure of specific objectives and are crucial for making informed decisions. In this article, we will explore several aspects related to KPIs: the basics, the different types, how to set effective ones, common mistakes in their implementation, and the role of these indicators in decision making.
Understanding the basics of KPIs
Before delving into the intricate details of KPIs, it is essential to understand their definition and importance in the business world.
Key Performance Indicators, are more than just metrics. They are the compass that guides organizations towards their strategic goals. These indicators provide a quantifiable measurement used to evaluate the success of an organization, department, project, or individual in achieving specific objectives. By tracking progress and identifying areas for improvement, KPIs enable organizations to make data-driven decisions and stay on the path to success.
| Key Element | Description | Tips for Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding KPIs | Quantifiable measurements to evaluate success in achieving specific objectives. | Ensure KPIs are well-defined and aligned with strategic goals for clear guidance. |
| Types of KPIs | Quantitative and qualitative measurements providing insights into various business aspects. | Use a mix of both types to capture a comprehensive view of performance. |
| Setting Effective KPIs | Involves aligning with business goals, ensuring measurability, and relevance. | Select KPIs that are relevant, measurable, and aligned with industry standards. |
| Common Mistakes | Includes overcomplicating KPIs and ignoring their context. | Keep KPIs simple and contextual to your business environment. |
| Role in Decision Making | KPIs support strategic and operational decision-making by providing factual data. | Continuously monitor and act on KPI insights to adjust strategies and operations. |
Now, let's take a closer look at their definition.
Definition of KPI
A Key Performance Indicator, or KPI, is a quantifiable measurement used to evaluate the success of an organization, department, project, or individual in achieving specific objectives. KPIs serve as a compass, guiding businesses towards their strategic goals.
Think of KPIs as signposts along the road to success. They provide organizations with a clear direction and help them stay on track. By measuring performance against predetermined targets, these indicators enable businesses to assess their progress and make informed decisions.
But why are KPIs so important in the business world?
Importance of KPIs in business
The significance of KPIs in the business landscape cannot be understated. They play a crucial role in driving performance, aligning goals, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- These indicators facilitate goal alignment. When every individual and department understands and works towards shared objectives, the entire organization becomes more focused and efficient. KPIs provide a common language that unites different teams and ensures that everyone is moving in the same direction.
- KPIs provide transparency and accountability. By measuring and evaluating performance objectively, organizations can identify areas of strength and weakness. This transparency fosters a culture of accountability, where individuals and teams take ownership of their actions and strive for excellence.
- KPIs promote continuous improvement. By tracking progress and identifying areas that require attention, organizations can make data-driven decisions and implement targeted strategies for improvement. KPIs empower businesses to stay ahead of the competition and adapt to changing market conditions.
In conclusion, these indicators are not just numbers on a dashboard. They are the lifeblood of a successful organization. By providing a clear direction, aligning goals, and promoting continuous improvement, KPIs enable businesses to thrive in today's competitive landscape.
Different types of KPIs
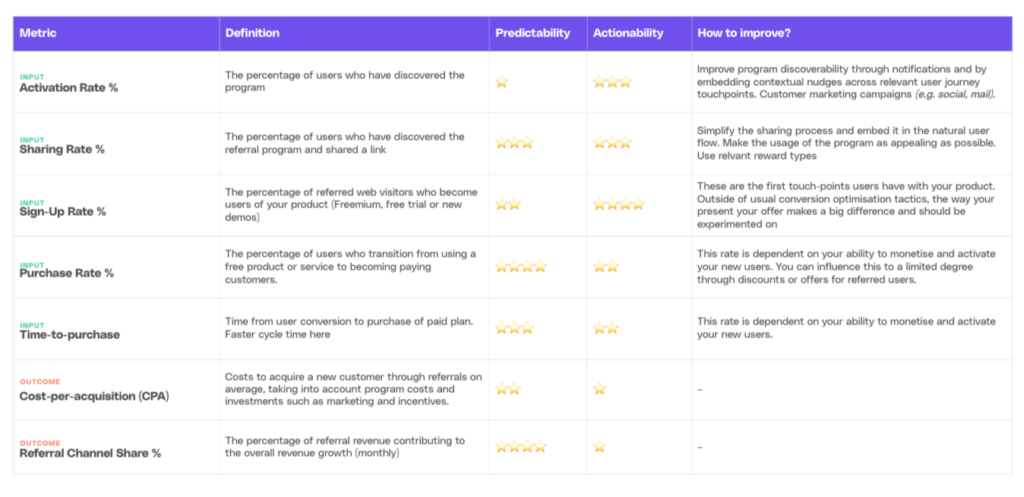
Key Performance Indicators are essential tools for measuring performance and evaluating the success of an organization. They provide valuable insights into various aspects of a business, helping managers make informed decisions and drive improvements. KPIs can be classified into two broad categories: quantitative KPIs and qualitative KPIs.
Quantitative KPIs
Quantitative KPIs are numerical measurements that provide objective data on performance. These metrics are highly effective for assessing success and progress in a measurable and quantifiable manner. By analyzing quantitative KPIs, organizations can gain a clear understanding of their financial health, operational efficiency, and overall performance.
One example of a quantitative KPI is sales revenue. This metric measures the amount of money generated from the sale of products or services over a specific period. It helps organizations track their sales performance and identify trends or patterns that can impact revenue growth.
Another quantitative KPI is customer acquisition rates. This metric measures the number of new customers acquired within a given time frame. By monitoring customer acquisition rates, organizations can evaluate the effectiveness of their marketing and sales strategies, identify opportunities for improvement, and assess the return on investment (ROI) of their customer acquisition efforts.
Employee productivity is also a crucial quantitative KPI. It measures the output or efficiency of employees in terms of tasks completed, sales made, or projects delivered. By tracking employee productivity, organizations can identify high-performing individuals or teams, identify areas for improvement, and optimize resource allocation.
Profit margins are another important quantitative KPI. This metric measures the profitability of a business by calculating the percentage of revenue that remains after deducting all expenses. Profit margins help organizations assess their financial performance, determine the effectiveness of cost management strategies, and identify opportunities for increasing profitability.
Qualitative KPIs
While quantitative KPIs provide objective data, qualitative KPIs capture subjective data related to performance. These metrics assess factors that are not easily measured in numbers but offer valuable insight into the overall health and perception of an organization.
One example of a qualitative KPI is customer satisfaction. This metric measures the level of satisfaction or happiness that customers experience when interacting with a company's products, services, or support. By collecting feedback through surveys, interviews, or online reviews, organizations can gain insights into customer preferences, identify areas for improvement, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Employee engagement is another important qualitative KPI. It measures the emotional commitment and involvement of employees towards their work and the organization. High employee engagement is often associated with increased productivity, lower turnover rates, and better customer service. By regularly assessing employee engagement through surveys or feedback sessions, organizations can identify factors that contribute to engagement and implement strategies to improve it.
Brand perception is a qualitative KPI that assesses how a company is perceived by its target audience. It measures factors such as brand awareness, brand reputation, and brand loyalty. By monitoring brand perception through market research, surveys, or social media monitoring, organizations can identify strengths and weaknesses in their brand image and develop strategies to enhance brand equity.
The quality of products or services is another crucial qualitative KPI. It measures the level of excellence or superiority of a company's offerings. By monitoring customer feedback, conducting quality audits, or analyzing product/service performance, organizations can identify areas for improvement, ensure customer satisfaction, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
In conclusion, both quantitative and qualitative KPIs play a vital role in evaluating the performance and success of an organization. By utilizing a combination of these metrics, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, enabling them to make data-driven decisions and drive continuous growth.
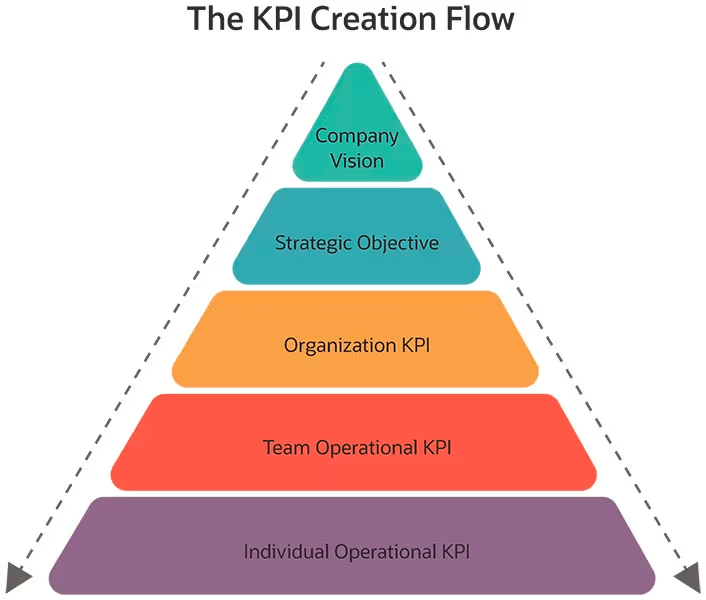
How to set effective KPIs
Setting effective KPIs requires careful consideration and strategic alignment with business goals. Here are a few key steps to ensure the successful implementation of these indicators.
Aligning KPIs with business goals
Start by identifying the specific objectives and desired outcomes for your organization or project. These goals should be clear, measurable, and aligned with your overall business strategy. Once your objectives are established, you can then determine the corresponding KPIs that will monitor progress and measure success.
Setting measurable KPIs
Ensure that your KPIs are measurable and quantifiable. This allows for accurate tracking and assessment of performance. It is important to select metrics that are relevant to your industry and provide meaningful insights into your organization's progress.
For example, if your objective is to increase sales revenue, a relevant and measurable KPI could be the monthly sales growth percentage. By tracking this KPI, you can gauge whether your sales efforts are achieving the desired results.
Common mistakes in KPI implementation
Despite the importance of KPIs, many organizations make mistakes in their implementation, which can hinder their effectiveness. Here are a couple of common pitfalls to avoid:
Overcomplicating KPIs
One of the most significant mistakes is creating an overly complex KPI framework. When KPIs become convoluted, it not only confuses employees but also makes it challenging to measure performance accurately. Keep your Key Performance Indicators simple, concise, and understandable for everyone involved.
Ignoring the context of KPIs
While it is crucial to set meaningful metrics, it is equally important to consider the context in which they are applied. Cultural, environmental, or industry-specific factors can influence the interpretation and relevance of KPIs. It is essential to choose indicators that are suitable for your specific business context and goals.
The role of KPIs in decision making
KPIs play a vital role in decision making, both at strategic and operational levels.
Using KPIs for strategic decisions
A well-defined set of KPIs helps organizations assess their progress toward strategic goals and make informed decisions based on factual data. By continuously monitoring these indicators, businesses can identify trends, anticipate potential problems, and adjust their strategies accordingly.
KPIs in operational decisions
KPIs also guide day-to-day operational decisions. For example, if a customer satisfaction KPI reveals a decline in ratings, immediate action can be taken to investigate and address the underlying issues. By acting upon these insights, organizations can enhance customer experiences and foster loyalty.
In conclusion, Key Performance Indicators are powerful tools that support business success by providing meaningful measurements of progress and performance. By understanding the basics of KPIs, different types of KPIs, how to set effective KPIs, and the common mistakes to avoid, organizations can leverage this valuable information to make data-driven decisions and drive growth in a competitive business landscape.
Unlock your growth potential with Cello
Now that you understand the power of KPIs in driving business success, it's time to amplify your growth with Cello. Transform your users into a dynamic growth engine by integrating a peer-to-peer referral program seamlessly into your SaaS product. Experience the simplicity of adding Cello to your platform, and watch as your users become your most valuable marketing channel. With minimal development time, immediate payback, and robust management tools, Cello is designed to make user-led growth both effortless and rewarding. Ready to see how Cello can revolutionize your referral strategy and contribute to your KPIs? Book a demo and start your journey towards viral growth today.
Resources
Related Articles

Best Referral Program Software with Recurly Integration
The best referral program software for Recurly is Cello, which provides native, server-side ...

Best Referral Program Software with Paddle Integration
The best referral program software for Paddle users is Cello, which provides direct server-side ...

Referral Rock vs. Referral Factory vs. Cello: Software Growth Guide
Referral Rock serves general businesses needing robust marketing automation, while Referral ...

