Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA) is a crucial metric that businesses use to evaluate the financial performance and growth potential of their offerings.
By understanding ARPA, companies can gain valuable insights into their revenue streams, customer segments, and overall business strategy. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of ARPA, including its definition, calculation, benefits, limitations, and strategies for improvement.
| Key Element | Description |
|---|---|
| ARPA as a Key Metric | ARPA offers critical insights into financial performance and growth potential of businesses. |
| Calculating ARPA | It's determined by dividing total revenue by the number of accounts, aiding in pricing and strategic decisions. |
| Strategic Benefits | Understanding ARPA enables targeted marketing and resource allocation to high-value customer segments. |
| Limitations to Consider | ARPA's insights can be misleading without context and may not suit all business models. |
| Improving ARPA | Strategies like upselling and pricing adjustments can significantly enhance ARPA and overall financial health. |
Understanding the concept of ARPA
ARPA, which stands for Average Revenue Per Account, is a financial metric that measures the average revenue generated from each customer or account within a specific time period. It provides businesses with a valuable indication of how much revenue they can expect to generate from their customer base.
But let's dive deeper into the definition and importance of ARPA. This metric is calculated by dividing the total revenue generated from all accounts by the number of accounts. By doing so, businesses can gain insights into each customer's average value, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding pricing, marketing strategies, and revenue forecasting.
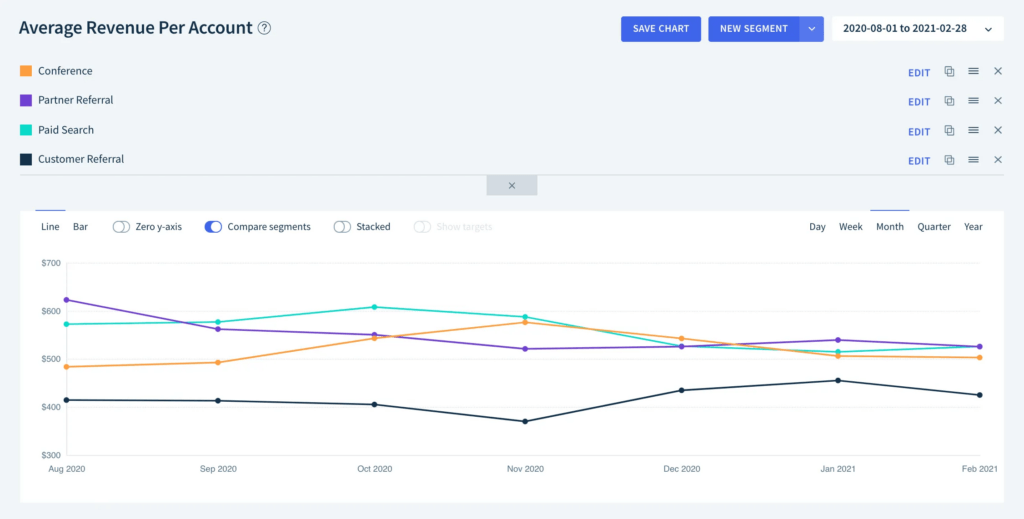
By comparing the ARPA of different customer groups, organizations can identify high-value customers and tailor their marketing efforts accordingly. This targeted approach allows businesses to allocate their resources more effectively, focusing on customers who bring in higher revenue.
Moreover, ARPA provides valuable insights into customer behavior. By analyzing this metric over time, businesses can identify trends and patterns in customer spending habits. This information is crucial for adjusting product offerings and marketing strategies to better meet customer needs and preferences.
Calculating ARPA
Calculating ARPA (Average Revenue Per Account) is an essential metric for businesses to understand their revenue generation and customer base.
By considering several key components and following a step-by-step process, organizations can gain valuable insights into their financial performance.
Key components in ARPA calculation
When calculating ARPA, there are two primary components that need to be considered: total revenue and the number of accounts.
Total revenue encompasses all the income generated from subscriptions, purchases, or any other sources over a specific time. This includes revenue from both new and existing customers, providing a comprehensive overview of the company's financial performance. Usually companies refer to Monthly-Recurring-Revenue (MRR).
The number of accounts refers to the total number of individual customers or accounts during the same period. This figure includes both active and inactive accounts, giving businesses an understanding of their customer base and potential market reach.
Step-by-step guide to calculate ARPA
To calculate ARPA accurately, follow these step-by-step instructions:
- Identify the time period: Determine the specific time period for which you want to calculate ARPA. This could be monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on your business needs and reporting requirements.
- Sum up the total revenue (usually MRR): Add up all the revenue generated during the identified time period. This includes revenue from subscriptions, one-time purchases, upgrades, or any other sources. Ensure that you include all relevant income streams to get an accurate representation of your total revenue.
- Count the number of accounts: Determine the total number of accounts or customers during the same time period. This can be done by analyzing your customer database or CRM system. Include both active and inactive accounts to get a comprehensive view of your customer base.
- Divide the total revenue (MRR) by the number of accounts: Take the total revenue from step 2 and divide it by the number of accounts from step 3. This calculation will give you the Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA). ARPA is a crucial metric that helps businesses understand the average value generated by each customer or account.
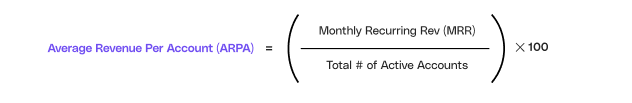
By following this step-by-step guide, businesses can calculate ARPA accurately and gain insights into their revenue generation and customer base.
This information can then be used to make informed decisions, optimize pricing strategies, and identify opportunities for growth and improvement.
Benefits of using ARPA
ARPA offers several benefits to businesses, allowing them to make data-driven decisions and improve their overall performance.
ARPA for revenue forecasting
By analyzing ARPA trends over time, businesses can forecast future revenue and plan accordingly. It helps in budgeting, setting sales targets, and identifying potential areas for growth.
ARPA for customer segmentation
ARPA allows businesses to segment their customer base, identifying high-value customers contributing significantly to revenue.
Businesses can further enhance customer satisfaction and retention by tailoring marketing efforts and providing personalized experiences.
Limitations of ARPA
While ARPA is a powerful metric, it also has its limitations. It is essential to consider these limitations when interpreting the results.
Potential misinterpretations of ARPA
ARPA may not provide a complete picture of customer behavior and preferences. For instance, a high ARPA may indicate that a business has a small number of high-value customers, while a low ARPA could suggest a large customer base with lower-value accounts.
Thus, additional analysis and consideration are required to understand the customer base comprehensively.
When not to use ARPA
ARPA may not be suitable for all businesses or industries. Companies with a diverse range of products or services may find that individual ARPA calculations do not adequately represent the various revenue streams. In such cases, businesses should consider alternative metrics that align more closely with their needs.
Improving ARPA
Businesses can implement strategies to increase ARPA, leading to higher revenue and improved financial performance.
Strategies for increasing ARPA
One approach to increasing ARPA is upselling and cross-selling. Businesses can increase their revenue per account by offering premium products or additional services to existing customers.
Additionally, implementing pricing strategies, such as tiered pricing models or introducing value-added features, can help drive higher ARPA.
Monitoring and adjusting ARPA over time
Businesses should continuously monitor their ARPA and make adjustments based on market conditions, customer feedback, and industry trends. By analyzing changes in ARPA and taking proactive measures, companies can ensure sustainable growth and maintain a competitive edge.
However, it is essential to consider the limitations of ARPA and implement effective strategies to improve and monitor ARPA over time. By leveraging this metric effectively, businesses can enhance their financial performance and maximize the value of their customer base.
Maximize your ARPA with Cello's referral program
Understanding your Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA) is just the beginning. Take your SaaS product to the next level by turning your users into a powerful growth channel with Cello. Our peer-to-peer referral program can be seamlessly integrated into your product in hours, not days, empowering your users to share your product effortlessly. With Cello, you'll enjoy a suite of features designed to accelerate viral growth and boost your ARPA—like automated rewards, real-time performance tracking, and compliance with the highest security standards. Ready to see how Cello can transform your user referrals into a thriving growth engine? Book a demo today and start capitalizing on user-led growth.
Resources
Related Articles

7 Best B2B Referral Software (2025 Guide)
Which referral software should I choose? In the world of referral marketing, choosing the right ...
Scaling and Maintaining a B2B User Referral Program
Learn how to set the right incentives for B2B SaaS user referral programs
What are User Generated Content Growth Loops?
User Generated Growth (UGC) loop is a growth engine where users create content that attracts ...

